Diamonds Explained
 There have been numerous books written in great detail about diamonds. In this article, we are going to summarize how diamonds are graded. Every diamond is unique and there are a number of factors which affect a diamonds beauty and therefore its value. These factors are known as a diamonds four C`s, which are clarity, colour, carat and cut. The four C`s are the internationally accepted set of standards by which a diamond is judged. These standards were first developed by the Gemological Institute of America ( GIA ). Established in 1931 the GIA is considered the global authority for diamond grading. Although the clarity, colour, carat and cut all interact with each other. It is generally accepted that the diamonds cut will have the greatest impact on the diamond’s beauty. Before purchasing a diamond or diamond ring it is recommended that you first set a budget. Then prioritise the four C`s in order of importance to you. For example, the colour difference between a D grade diamond and an E grade diamond cannot be seen by the naked eye. However, the difference in price will be substantial. Therefore by prioritising the four C`s, you will be able to choose the perfect diamond for you.
There have been numerous books written in great detail about diamonds. In this article, we are going to summarize how diamonds are graded. Every diamond is unique and there are a number of factors which affect a diamonds beauty and therefore its value. These factors are known as a diamonds four C`s, which are clarity, colour, carat and cut. The four C`s are the internationally accepted set of standards by which a diamond is judged. These standards were first developed by the Gemological Institute of America ( GIA ). Established in 1931 the GIA is considered the global authority for diamond grading. Although the clarity, colour, carat and cut all interact with each other. It is generally accepted that the diamonds cut will have the greatest impact on the diamond’s beauty. Before purchasing a diamond or diamond ring it is recommended that you first set a budget. Then prioritise the four C`s in order of importance to you. For example, the colour difference between a D grade diamond and an E grade diamond cannot be seen by the naked eye. However, the difference in price will be substantial. Therefore by prioritising the four C`s, you will be able to choose the perfect diamond for you.
Diamond Clarity
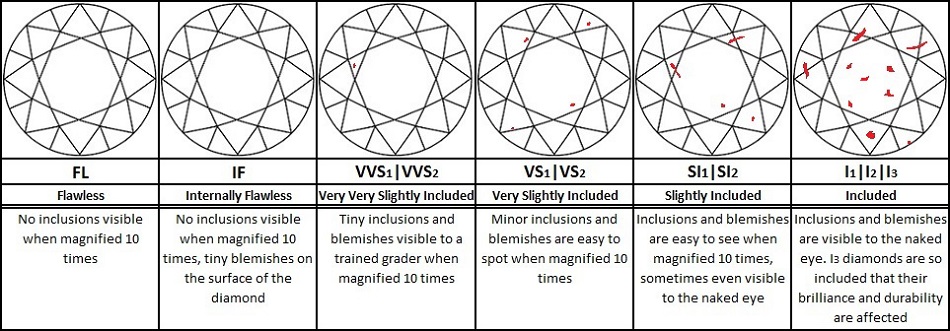
Diamonds are made deep within the earth`s crust under huge pressure. As a result, virtually all diamonds will contain some level of imperfection. It is extremely rare for a diamond to be classed as flawless or even internally flawless. It is estimated that only one in every five thousand diamonds graded are classed as flawless. It has also been estimated that around a third of all diamonds sold have a clarity grading of SI1 or SI2. This grade of inclusion cannot normally be seen by the naked eye. So to give an idea ( as each diamond is unique ) of the difference between a SI1 clarity grade and a VS1 clarity grade. A VS1 clarity grade diamond would typically be about twice the cost of a SI1 diamond. Of course, this would be subject to the colour, cut and carat of each diamond being identical. As a general rule, clarity becomes more important for diamonds over 1ct in size. As it is easier to see any imperfections in a larger diamond.
Diamond Colour
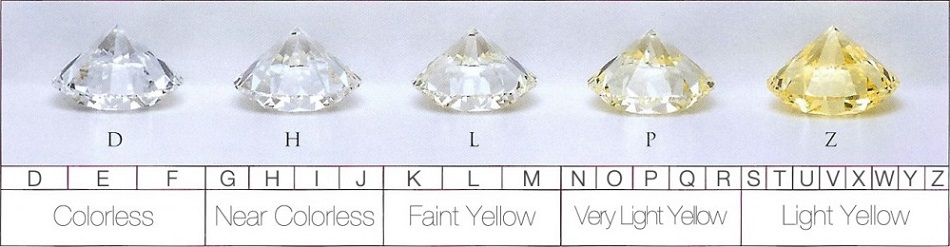
Diamonds not only formed in white but also include yellow, pink, blue, brown, orange, red, purple, grey and black. These coloured diamonds are known as fancy diamonds and are graded on separate colour scales. White diamonds are graded on a scale of D to Z, with D being colourless and Z being light yellow. Diamonds are graded by gemologists in a lab where the lighting is controlled and using a set of master diamonds as in the above photo. To the naked eye, no difference can be seen from grade D to grade J, under normal lighting and without a set of master diamonds. However, the price difference between these two grades would typically be double. It is from grade K onwards that the colour differences can be seen under normal lighting conditions.
Once a diamond has been set in a ring or piece of jewellery, it becomes much harder to see the colour if there is any present. This is partly due to the position of the diamond, which will be viewed from the table when mounted in a setting. As opposed to being viewed from the pavilion, as gemologists do when colour grading a diamond. When viewed from the table the fire and brilliance of a diamond is at its height. Also, a yellow gold setting will make any yellow present in a diamond less obvious. Whereas a white metal setting will highlight any yellow colour in a diamond. So in general colour grades D to J are considered suitable for a platinum or white gold setting. While colour grades K to Z would be more suitable for a yellow gold setting.
Just as with clarity, a diamonds colour becomes more important as the carat size increases, typically above 1ct. As it becomes easier to see any colour present in a larger diamond.
Diamond Carat

A diamond carat is the measurement of a diamond`s weight. As opposed to the actual size of the diamond, which is commonly believed. A 1 carat diamond is 200 milligrams. This standardisation of diamond weight was first introduced in America in 1913 and thereafter was accepted worldwide. Diamonds weighing less than 1 carat, are measured in points. With there being 100 points in a single carat so for example, a diamond weighing 50 points would be half a carat. The vast majority of diamonds sold weight 1 carat or less.
Diamond Cut
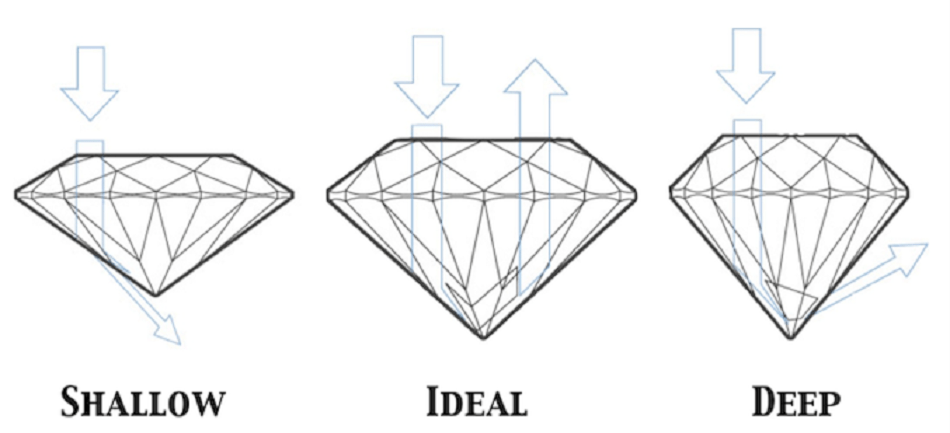
Diamond cut is generally accepted as having the most impact of all the four C`s on a diamond`s beauty. Diamond cut refers to the proportions and reflective quality of a diamond. It does not refer to the shape of a diamond. When a diamond is cut too shallow the light entering from the table is reflected back out through the bottom of the pavilion. Whereas when a diamond is cut too deep the light entering through the table is reflected out through the side of the pavilion. In both of these cases, the diamond will appear dull. In the case of a well-cut diamond, the light entering through the table is reflected off each of the pavilions facets with most of this light leaving through the crown. Resulting in a bright and lively diamond, known as a diamonds fire and brilliance. Diamond cut is graded on a scale of ideal, excellent, very good, good, fair and poor.
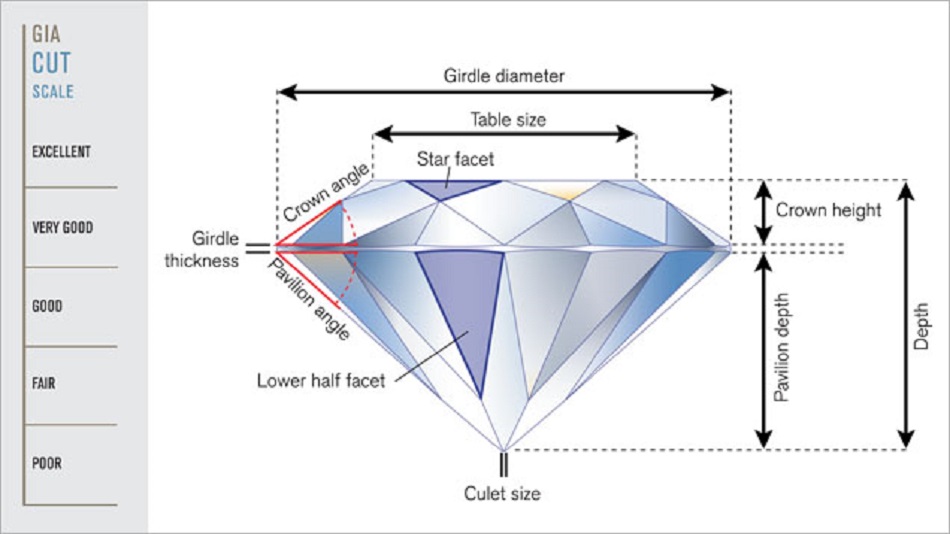
Diamond Shape Chart

You can also get in touch with Carusjewellery.com on Facebook , where you may leave any comments or questions you may have about this article.

